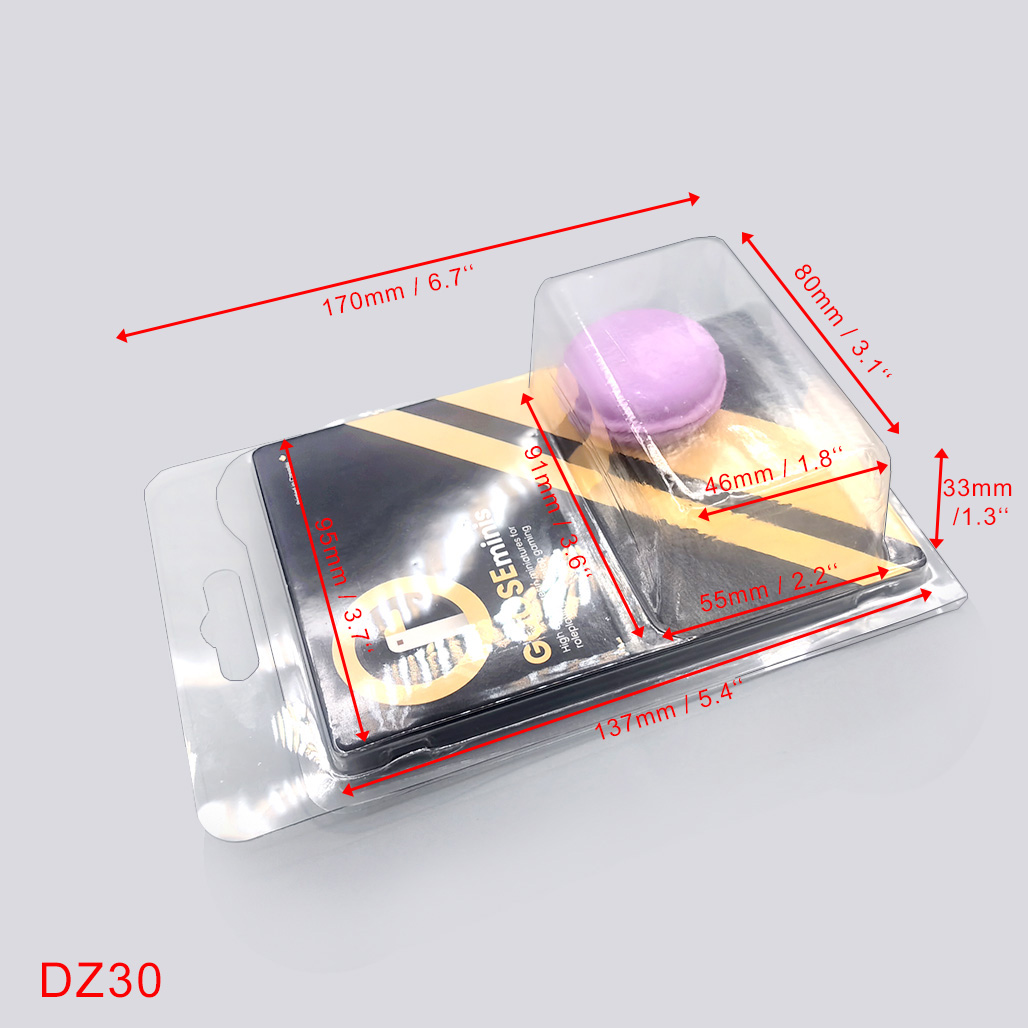
Vacuum packaging is a general term for plastic products produced using vacuum molding technology and packaged with corresponding equipment. The products mainly include: bubble shells, trays, vacuum boxes, and synonyms include: vacuum covers, bubble covers, etc.
Blister packaging materials and their characteristics
PVC sheets have high toughness and are not easy to burn. When burned, chlorine gas is produced, which has a certain impact on the environment. PVC is easy to heat and can be sealed using sealing machines and high-frequency edge banding. It is the main raw material for producing transparent vacuum molded products. PVC film is a widely used and popular material. PVC film can be divided into two types: environmentally friendly and non environmentally friendly. It can be made into various vacuum packaging products such as transparent, colored, anti-static, gold-plated, flocked, etc. Its main characteristics are high transparency, good surface gloss, few crystal points, small water marks, wide use, strong impact resistance, and easy molding. The products are widely used for packaging of toys, food, electronic products, medicine, electrical appliances, gifts, cosmetics, stationery, and other products.

Two PS hard sheets have low density, poor toughness, are prone to combustion, and produce styrene gas (a harmful gas) during combustion, so they are generally used to produce various industrial vacuum pallets. PS sheet is a new type of environmentally friendly packaging material that has developed in recent years. With its excellent thermal forming performance, good environmental and hygiene performance, it is widely used in medicine, food, toys, and electronics.
Three PET hard sheets have good toughness and are a new type of material developed in recent years. Due to its excellent toughness, high strength, high transparency, and recyclability, it is easy to burn and does not produce harmful gases during combustion. As an environmentally friendly material, PVC has gradually been phased out, but its price is high. Suitable for high-end vacuum molded products, PET material is generally required for vacuum molded shell in European and American countries, but its high hot melting point poses great difficulties for high cycle packaging.

Four PETG materials are used to solve the problem of high hot melting point of PET materials. People composite a layer of PVC film on the surface of PET, named PETG, but the price is higher. Mainly used in electronics, food, toys, color box windows, collar holders, shoe packaging, etc.
Five PP sheets are mainly made of polypropylene resin as the main raw material, with various process color masterbatches, toughening agents, and brighteners added. They are made through mixing, plasticizing extrusion, three roll pressing, cooling, traction, and winding processes. PP sheets have the characteristics of being non-toxic, odorless, hygienic, with high mechanical strength and good barrier properties, and can be used for packaging in industries such as industry, agriculture, and fruits. The surface of the tray made of PP anti slip sheets is smooth and beautiful, which is highly welcomed by users. PP sheet is also suitable for packaging of high cold resistant frozen foods, such as ice cream boxes, dumplings boxes, dumplings boxes, etc

PP vacuum molding has the advantages of environmental protection, aesthetics, silk screen printing, offset printing, hot stamping, high temperature resistance, low temperature resistance, high transparency, resistance to bending and easy folding, product compliance with food testing standards (or not required), and microwave capability.
The disadvantages of PP include low dimensional accuracy, insufficient rigidity, poor weather resistance, and susceptibility to copper damage. It exhibits post shrinkage and is prone to aging, brittleness, and deformation after demolding.

Blister packaging production process
1: Mold making and processing: According to the requirements or sample specifications, the first step is to make a vacuum plastic mold. Generally, gypsum is used to make vacuum plastic packaging molds, but wooden and metal carved products are also used as molds. After the gypsum mold is made, it is allowed to dry naturally or completely. Then, according to the specific situation of the product surface’s convexity and concavity, 1-2 millimeters of drill flowers are used to drill many small holes in the low and concave areas that do not affect the product packaging shape. If it is a packaging box or similar product, some small holes need to be drilled on the four sides so that air can be extracted during vacuum plastic production. After drilling the holes in the mold, the gypsum mold needs to be hardened. The hardening treatment method is to saturate with concentrated alum. Soak in liquid and let it dry.

2: After the mold is completely dried, place the mold onto the upper iron plate of the vacuum chamber. Then, according to the size of the mold, load the plastic sheets into suitable specifications and sizes. Then, place the sheet material into a heated wooden cabinet to fix it completely. Finally, place the wooden cabinet and plastic sheets on a constant temperature furnace for softening treatment.
3: Place the softened plastic sheets together with the wooden cabinet in a vacuum chamber, activate the suction switch to clean the air inside the vacuum chamber, and wait for the plastic sheets to cool down to obtain the same concave packaging or process mold as the mold.
4: Vacuum packaging and sorting; The finished product is obtained by trimming and organizing the edges of the produced product, which can then be packaged and sold.
Quotation for blister packaging
The unit price of vacuum molding=product material cost+energy consumption+labor and transportation+profit
Energy consumption: Vacuum forming is achieved through thermal processing, which consumes a relatively large amount of electricity compared to other industries, approximately 8% of the material cost of the product. Labor consumption: Vacuum forming mainly relies on machine production, with less labor, approximately 10% of the material cost of the product. Transportation: Depending on the distance from the customer to our factory, profit: The net profit of vacuum forming factories is generally very low, 12% -20%, depending on the payment term. 30 day settlement is 14%. Material cost: The calculation of product material cost is relatively complex. Before calculating, first clarify the following data:

Raw material price: Determine the material and grade to be used based on the product’s purpose, and search for the lowest price supplier for that material. Film thickness: Predict the thickness of the film required for the product to be made, and determine the layout quantity based on the thickness and shape of each forming part. Calculate how many molds can be arranged in a plate based on the external size and shape of the product. Dense arrangement will reduce product quality, while sparse arrangement will increase material loss and increase costs. Material loss rate: The main factors include product shape, quantity, and the degree of compatibility between the external size and the vacuum molding machine chassis. The more square the shape and larger the output, the smaller the loss rate

Formula for calculating material costs
Product material cost=1 ton raw material price/1 ton raw material finished product quantity
1 ton of raw material production quantity=1 ton of raw material length/(blister template length+4cm to 15cm stretching edge) X layout quantity X (100% – material loss rate)
1 ton of raw material length=1 ton/material density/film thickness/width (vacuum molded chassis width)
The material density (PVC is 1.36T/m3), vacuum molded chassis width (0.51-1.20M), template length, and other four parameters are estimated based on professional experience